Patient Education
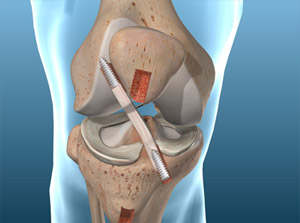
ACL Reconstruction
This procedure repairs your knee after a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (commonly called the "ACL"). This ligament is in the center of the knee. It helps anchor the femur to the tibia. This surgery can allow you to regain normal knee function.
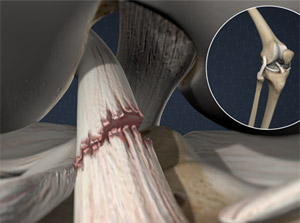
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear (ACL Tear)
This injury is a tearing of the ACL ligament in the knee joint. The ACL ligament is one of the bands of tissue that connects the femur to the tibia. An ACL tear can be painful. It can cause the knee to become unstable.
Patellar Tracking Disorder
This is a problem with the alignment of the patella (the bone at the front of the knee, commonly called the "kneecap"). With this disorder, the patella shifts out of its normal track as you bend or extend your knee.
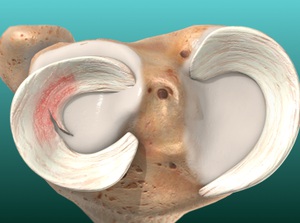
Partial Meniscectomy
The meniscus is a cushion of cartilage. There are two in each knee. If one of these shock absorbers is worn out or hurt, you may need a partial meniscectomy to remove the damaged areas.
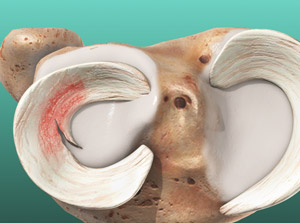
Meniscus Tear
This is a common injury of the knee. Your knee joint is cushioned by two c-shaped wedges of cartilage called the "menisci." Each individual cushion is called a "meniscus." This injury is a tear of one of these cushions.
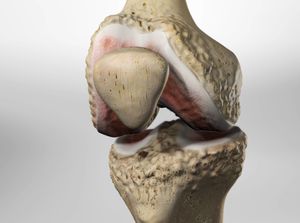
Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative arthritis, is a gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Cartilage is a tough, flexible connective tissue that protects the ends of bones in the joints. Osteoarthritis is common in the knees because the knees bear the weight of the body. Osteoarthritis of the knee can severely impact a person's lifestyle.
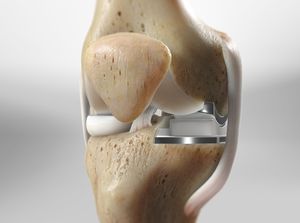
Partial Knee Replacement (using OXFORD® implant)
Unlike total knee replacement surgery, this less invasive procedure replaces only the damaged or arthritic parts of the knee. The OXFORD® unicompartmental knee uses metal and plastic implants designed to potentially last longer and wear down less easily than traditional implants.

Total Knee Replacement
This procedure restores function to a severely damaged knee. Most commonly, it is used to repair a knee that has been damaged by arthritis. During the procedure, the surgeon replaces the damaged portions of the knee with artificial parts. These parts consist of a metal femoral component, a metal tibial component and a plastic spacer. A small plastic patellar component may also be used.
Joint Replacement Surgery: Knee
The key to a successful surgery and recovery is knowledge and preparation! You have a vital role to play along with your surgeon and their team, anesthesiologists, nurses and physical therapists. Reading, understanding, and implementing the information provided to you in your joint replacement manual and the associated videos will help prepare you for your joint replacement journey and give you the knowledge and tools to manage successfully after your surgery.

Preparing For Surgery
Welcome
Preparing My Home
What to Expect on Your Day of Surgery
Postoperative Care
Pain Management pg. 17
Compression Stockings and Wraps pg. 19
Dressings pg. 20
How to Prevent a Blood Clot
Managing Constipation With Narcotics pg. 21
Postoperative Complications pg. 22
Bed Transfers pg. 33
How to use My Walker or Cane pg. 34
Stopping the spread of MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) pg. 58
Frequently Asked Questions pg. 64
Home Exercises
Ankle Pumps pg. 36
Quad Sets pg. 37
Heel Slides pg. 38 & pg. 43
Short Arc Quads pg. 39
Straight Leg Raise pg. 40
Long Arc Quads pg. 42
Knee Extension Stretch pg. 44
Mini Squats pg. 45
Calf Stretch pg. 46
Heel Raises pg. 47
